Developing innovative packaging solutions is crucial for brand differentiation, but many businesses struggle to find the right manufacturing partner. You’re looking for quality, innovation, and cost-effectiveness – all while navigating international collaboration challenges.
Working with a Chinese packaging factory to develop innovative solutions requires careful partner selection, clear communication, collaborative design processes, and strategic project management. Success depends on choosing experienced manufacturers with R&D capabilities, establishing transparent workflows, and maintaining quality control throughout development.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through every step of the collaboration process, from initial partner selection to final production.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Should You Look for When Selecting a Chinese Packaging Factory?
Choosing the right manufacturing partner is the foundation of successful packaging innovation. Your factory selection directly impacts product quality, development timeline, and long-term business success.
Look for factories with essential certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 14001, FSC Chain-of-Custody), proven production capabilities, financial stability, and robust quality control systems. Geographic location, advanced technology, and diversified client portfolios are equally important selection criteria.

Essential Manufacturing Certifications
Quality and Environmental Standards
Prioritize factories with ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management), FSC Chain-of-Custody (responsible sourcing), and G7 Master Certification (color calibration consistency). These certifications demonstrate systematic quality management and adherence to international standards.
Industry-Specific Compliance
Ensure your chosen factory tests materials and processes for FDA and EU compliance. They should source materials from FSC-certified mills and implement rigorous material inspection protocols.
Production Capabilities Assessment
Technology and Equipment
Evaluate advanced printing technology, specialized equipment capabilities, and ability to produce various packaging formats. Look for factories with AI-driven visual inspection systems and automated production lines.
Capacity and Scalability
Assess production capacity including number of production lines, daily output capabilities, and ability to handle your expected order volumes. Consider their ability to scale with your business growth.
| Assessment Factor | What to Look For | Red Flags |
|---|---|---|
| Certifications | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, FSC, G7 Master | No international certifications |
| Equipment | Advanced printing, AI inspection systems | Outdated manual processes |
| Financial Health | Reinvestment in infrastructure | Single-industry dependence |
| Location | Access to major hubs (Shenzhen, Guangzhou) | Remote locations with poor logistics |
Financial Stability and Business Track Record
Diversification Strategy
Choose manufacturers serving multiple industries rather than single-industry specialists. This indicates better stability during market downturns and reduces business risk.
Investment in Innovation
Look for companies that reinvest profits into new infrastructure and technology. This demonstrates commitment to continuous improvement and long-term viability.
Geographic Considerations
Consider factory location strategically. Shenzhen and Guangzhou offer advanced printing technology but higher costs, while regions like Longgang (Cangnan-Wenzhou) provide competitive pricing with mature technologies.
How Do You Initiate the Collaboration Process?
Starting your collaboration correctly sets the tone for the entire project. Chinese business culture emphasizes relationship-building, making the initial engagement phase crucial for long-term success.
Begin with relationship building, conduct thorough due diligence including factory audits, establish multiple communication channels, and create comprehensive project documentation. Cultural understanding and clear requirements documentation are essential for successful initiation.

Building Strong Relationships
Cultural Understanding First
Chinese culture is heavily relationship-based, so building strong personal relationships is crucial for success. Invest time in understanding business culture, respect hierarchical structures, and acknowledge Chinese festivals and cultural events.
In-Person Engagement
Visit the factory in person when possible to understand manufacturing processes, negotiate costs, and protect your business interests. Virtual tours can substitute when travel isn’t feasible.
Multiple Contact Points
Establish at least two points of contact at the factory and set up multiple communication methods including WeChat, email, and video calls for different types of communication.
Comprehensive Due Diligence
Factory Audit Process
Conduct thorough factory audits through in-person visits or virtual tours. Observe pressrooms, finishing areas, raw material warehouses, and quality control systems. Partner with experienced inspection companies in China for independent factory evaluations.
Reference Verification
Request client references, particularly from companies with similar specifications or industry challenges. Verify the factory’s track record with international clients and their ability to meet quality standards.
Trial Order Strategy
Conduct trial orders of 200-500 units to evaluate real-world performance before committing to larger volumes. This helps assess quality, communication, and delivery capabilities.
Initial Engagement Documentation
Detailed Project Requirements
Prepare comprehensive specifications covering dimensions, tolerances, material grades, color references (Pantone or Lab), finishing requirements, and handling instructions. Provide samples or prototypes to set benchmarks.
Comprehensive RFQ Development
Submit detailed requests for quotation including product specifications (size, material, quantity, colors), payment terms, shipping requirements, and timeline expectations. Be specific about customization needs and special requirements.
What Are the Key Stages of the Development Process?
The development process follows a structured approach that balances innovation with manufacturability. Each stage requires specific deliverables and quality checkpoints to ensure successful outcomes.
The development process includes five key stages: project initiation and planning, design and development, prototyping and testing, production preparation, and launch execution. Each stage involves collaborative work between your team and the factory’s engineering experts.
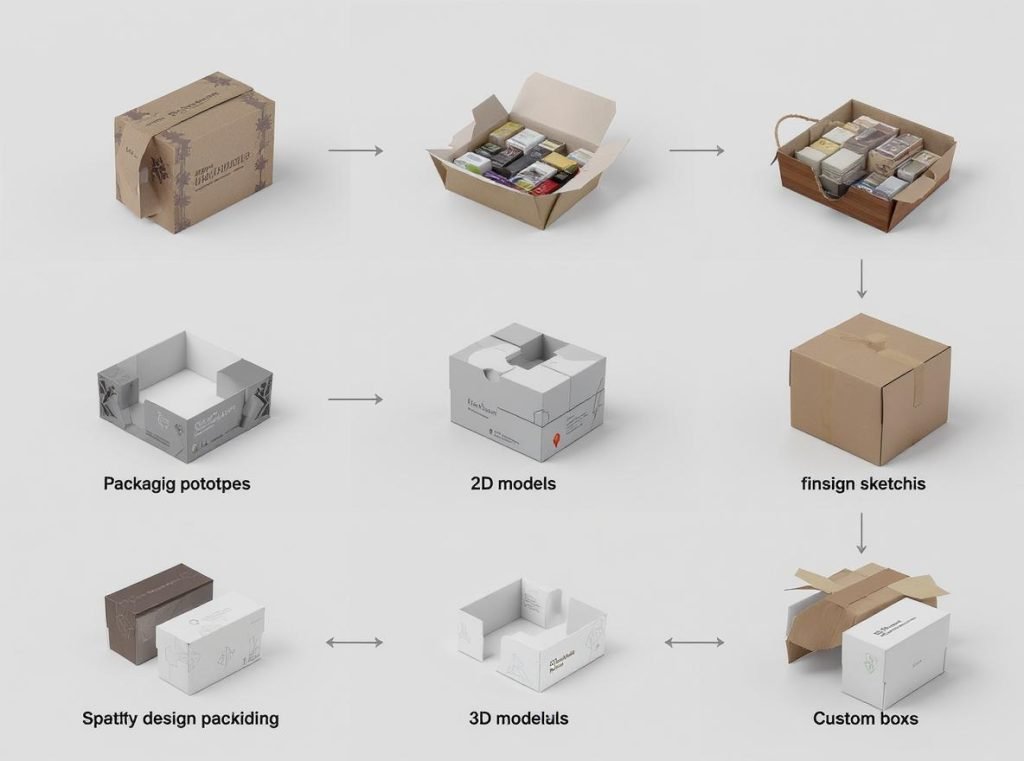
Stage 1: Project Initiation and Planning
Comprehensive Kickoff Meeting
Conduct kickoff meetings with all stakeholders including internal teams, co-packers, logistics coordinators, and plant managers. This ensures everyone understands project objectives and constraints from the beginning.
Product Requirements Analysis
Define your product concept clearly, considering customer needs, market positioning, and technical requirements. Conduct market research to understand trends and consumer preferences that will inform packaging design decisions.
Resource Allocation Planning
Establish project timelines, budget allocations, and resource requirements. Account for Chinese holidays and seasonal production variations in your planning.
Stage 2: Design and Development
Collaborative Design Development
Work with the factory’s design team to create initial concepts based on your requirements and market research. This iterative process should include regular feedback loops and design refinements.
Cost Analysis and Material Selection
Perform thorough cost analysis considering material costs, production processes, and logistics. Select appropriate packaging materials based on product protection needs, sustainability goals, and budget constraints.
Technical Feasibility Assessment
Evaluate each design concept for manufacturing feasibility, scalability potential, and quality control requirements.
Stage 3: Prototyping and Testing
Rapid Prototyping Capabilities
Leverage Chinese manufacturers’ rapid prototyping capabilities using 3D printing, CNC machining, and other advanced technologies. This allows for quick iterations and design validation.
Comprehensive Testing Protocol
Conduct functional testing including drop tests, compression tests, and shelf-life simulations to ensure packaging withstands storage and transit conditions.
Consumer Validation
Perform consumer testing to validate design concepts and gather feedback on packaging performance, functionality, and user experience.
Stage 4: Production Preparation
Manufacturing Process Optimization
Work with the factory to optimize production processes for efficiency and quality. This includes tooling design, production line setup, and quality control protocols.
Trial Production Runs
Conduct small-scale production runs to validate the manufacturing process and identify any issues before full-scale production. This helps prevent costly problems during mass production.
How Do You Ensure Quality Control Throughout Development?
Quality control is paramount when working with international manufacturers. Implementing robust quality systems prevents costly mistakes and ensures consistent results throughout the development process.
Implement a comprehensive quality control system including supplier vetting, multi-stage inspection processes, statistical process control, and AI-driven visual inspection. Pre-production, during production, and pre-shipment inspections are essential quality checkpoints.

Pre-Production Quality Measures
Supplier Vetting and Audits
Conduct comprehensive supplier assessments including factory audits, capability reviews, and compliance verification. Partner with experienced inspection companies in China for independent factory evaluations.
Material Standards and Sourcing
Establish clear quality standards for materials, processes, and finished products. Reputable manufacturers source materials from certified suppliers and implement rigorous incoming material inspection.
Pre-Production Inspection (PPI)
Evaluate prototypes and samples before mass production begins. This includes material verification, dimensional checks, and functional testing.
In-Process Quality Control
Statistical Process Control (SPC)
Leading factories implement SPC techniques using real-time data from inline measurement devices to track print density, color consistency, and cut precision. Automated alerts prompt immediate intervention when readings drift beyond tolerances.
During Production Inspection (DPI)
Monitor quality during manufacturing to catch defects early. This includes regular sampling, process monitoring, and immediate corrective actions when issues are identified.
AI-Driven Visual Inspection
Advanced factories integrate AI-powered camera systems on finishing lines to detect defects like scratches, misalignments, and off-register printing at rates exceeding manual inspection capabilities.
Final Quality Assurance
Pre-Shipment Inspection (PSI)
Conduct final quality verification before shipping. This comprehensive check ensures products meet all specifications and quality standards.
Functional Performance Testing
Perform comprehensive testing including:
- Drop tests for durability assessment
- Compression tests for strength validation
- Environmental tests for stability confirmation
- User experience testing for functionality
| Quality Stage | Inspection Type | Key Focus Areas |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Production | PPI | Material verification, prototype validation |
| During Production | DPI | Process monitoring, defect prevention |
| Pre-Shipment | PSI | Final specification compliance |
What Communication Strategies Ensure Project Success?
Effective communication bridges cultural and geographical gaps, ensuring your innovative packaging project stays on track and meets expectations despite language barriers and cultural differences.
Use clear, simple language with visual aids, establish multiple communication channels, implement written confirmations for all decisions, and invest in relationship building. Cultural sensitivity and structured communication protocols are essential for success.

Language and Cultural Considerations
Simplify Communication Methods
Use clear, concise language with short sentences and simple vocabulary. Avoid technical jargon, slang, and complicated terms that may be difficult to translate. Structure communication using numbered points and bullet lists for clarity.
Cultural Sensitivity Awareness
Understand that Chinese communication tends to be indirect, and “no” is rarely said directly. The concept of “face” (mianzi) is crucial – avoid public criticism or blunt rejection. Respect hierarchical structures and work through established contact persons.
Visual Communication Tools
Use diagrams, photos, and visual aids to overcome language barriers. Provide clear product samples and detailed technical drawings to minimize misunderstandings.
Effective Communication Practices
Multiple Communication Channels
Establish various communication methods including email for formal documentation, WeChat for quick updates, video calls for complex discussions, and project management tools for tracking progress.
Written Confirmation Protocol
Always confirm verbal agreements in writing and request written summaries of key decisions. Use bilingual documentation when possible to ensure clear understanding on both sides.
Regular Communication Schedule
Maintain consistent communication through:
- Weekly progress updates
- Monthly strategic reviews
- Quarterly business reviews
- Annual partnership assessments
Building Long-Term Relationships
Relationship Investment Strategy
Invest time in building personal relationships through virtual introductions and acknowledgment of Chinese festivals and cultural events. Strong relationships lead to better accommodation of urgent requests and pricing negotiations.
Performance Review Process
Conduct periodic reviews to address any concerns and maintain open communication channels. Encourage questions and clarifications to prevent misunderstandings.
How Do You Manage Costs and Timelines Effectively?
Successful packaging development requires careful cost management and realistic timeline planning. Understanding cost structures and production schedules helps prevent budget overruns and delays.
Understand comprehensive cost structures including materials, design complexity, and logistics. Plan for manufacturing timelines of 5-40 days plus shipping, account for Chinese holidays, and negotiate comprehensive packages rather than focusing solely on lowest prices.

Cost Management Strategies
Understanding Complete Cost Structure
Packaging costs include materials, design complexity, production processes, waste reduction, and logistics. Focus on material optimization by right-sizing packaging and avoiding overuse of materials.
Hidden Cost Awareness
Be aware of additional costs not always included in initial quotations, such as tooling, freight to port, customs charges, and special processing fees. Chinese suppliers often quote attractive base prices but add various charges later.
Negotiation Approach
Negotiate comprehensive packages including price, quality, delivery schedule, and payment terms rather than focusing solely on lowest price. Bulk ordering can reduce per-unit costs, but balance this against inventory needs.
Timeline Management
Production Planning Reality
Manufacturing timelines in China typically range from 5-40 days depending on complexity and order quantity. Plan for longer initial runs when specialized molds or intricate assembly is required.
Holiday Considerations
Account for Chinese holidays that significantly impact production schedules:
- Chinese New Year (January/February): Plan orders 2-3 months in advance
- Golden Week (October): Schedule shipments 4-6 weeks prior
- Dragon Boat Festival (June): Expect 3-5 day delays
- Mid-Autumn Festival (September/October): Production often slows 1-2 weeks before
Shipping and Logistics Planning
Factor in shipping times: air freight to US takes 3-7 days, while sea freight requires 30+ days. Include customs clearance time and domestic delivery in your timeline planning. Door-to-door delivery from China typically takes 10-12 weeks for complex packaging projects.
What Are the Common Challenges and How Can You Overcome Them?
Working with Chinese packaging factories presents unique challenges, but understanding these obstacles helps you prepare effective solutions and maintain successful partnerships.
Common challenges include communication barriers, quality control issues, cost overruns, intellectual property concerns, and supply chain disruptions. Success requires proactive planning, comprehensive contracts, multiple safeguards, and flexible problem-solving approaches.
Communication and Language Barriers
Challenge: Language differences leading to misunderstandings about specifications, timelines, and quality requirements.
Solutions:
- Use professional translation services and bilingual intermediaries
- Employ simple, clear language with visual aids
- Implement structured communication protocols with written confirmations
- Consider hiring local representatives who understand both business culture and technical requirements
Quality Control Issues
Challenge: Inconsistent quality standards, lack of standardization across factories, and insufficient quality control measures.
Solutions:
- Establish clear quality standards and provide detailed specifications
- Implement multi-stage inspection processes (pre-production, during production, pre-shipment)
- Partner with third-party inspection companies for independent quality verification
- Conduct regular factory audits and maintain close oversight of production processes
Cost and Timeline Overruns
Challenge: Unexpected cost increases, extended lead times, and hidden charges not included in initial quotations.
Solutions:
- Negotiate comprehensive contracts with clear penalty clauses for delays
- Plan for 10-12 week door-to-door timelines for complex projects
- Avoid paying large upfront payments; structure payments based on delivery milestones
- Account for Chinese holidays and seasonal production variations in planning
Intellectual Property Protection
Challenge: Risk of design theft, unauthorized production continuation, and confidentiality breaches.
Solutions:
- Implement comprehensive NDAs and intellectual property agreements
- Use legal protections including patents, trademarks, and confidentiality clauses
- Maintain control over critical design elements and tooling
- Work with reputable suppliers who demonstrate respect for IP rights
Supply Chain Disruptions
Challenge: Material shortages, shipping delays, and geopolitical factors affecting production.
Solutions:
- Diversify supplier base to reduce dependency on single sources
- Maintain buffer inventory for critical materials
- Develop contingency plans for supply chain disruptions
- Consider nearshoring alternatives for reduced risk exposure
Summary
Working with a Chinese packaging factory to develop innovative solutions requires balancing significant advantages of cost-effectiveness and manufacturing capabilities with careful management of inherent risks. Success depends on thorough preparation, structured supplier selection, clear communication protocols, and comprehensive quality control systems.

Ready to transform your packaging vision into reality? Contact Acreet today to discuss your custom packaging needs and discover how our experienced team, advanced manufacturing capabilities, and proven quality systems can help bring your innovative packaging solutions to life with reliable manufacturing excellence.


