When you’re selecting corrugated packaging for your business, understanding how much vertical load your boxes can handle is crucial for preventing costly damage and ensuring efficient shipping. The ECT rating gives you the exact measurement you need to make informed decisions.
The ECT (Edge Crush Test) rating measures the edgewise compressive strength of corrugated board, directly determining how much vertical force your boxes can withstand before collapsing. Higher ECT ratings mean superior stacking strength and load-bearing capacity, making them essential for palletized shipments and warehouse storage where boxes are stacked on top of each other.
Let’s explore how ECT ratings impact your packaging performance and help you choose the right strength for your specific shipping needs.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat Is the ECT Rating and How Is It Measured?
Understanding ECT ratings starts with knowing exactly what this critical test measures and why it’s become the industry standard for corrugated packaging.
The ECT (Edge Crush Test) measures the maximum compressive force that a corrugated material can withstand when pressure is applied perpendicular to the flute direction. The test involves compressing a rectangular specimen between two rigid platens until it reaches peak load failure, with results expressed in pounds per lineal inch (lb/in) or kiloNewtons per meter (kN/m).
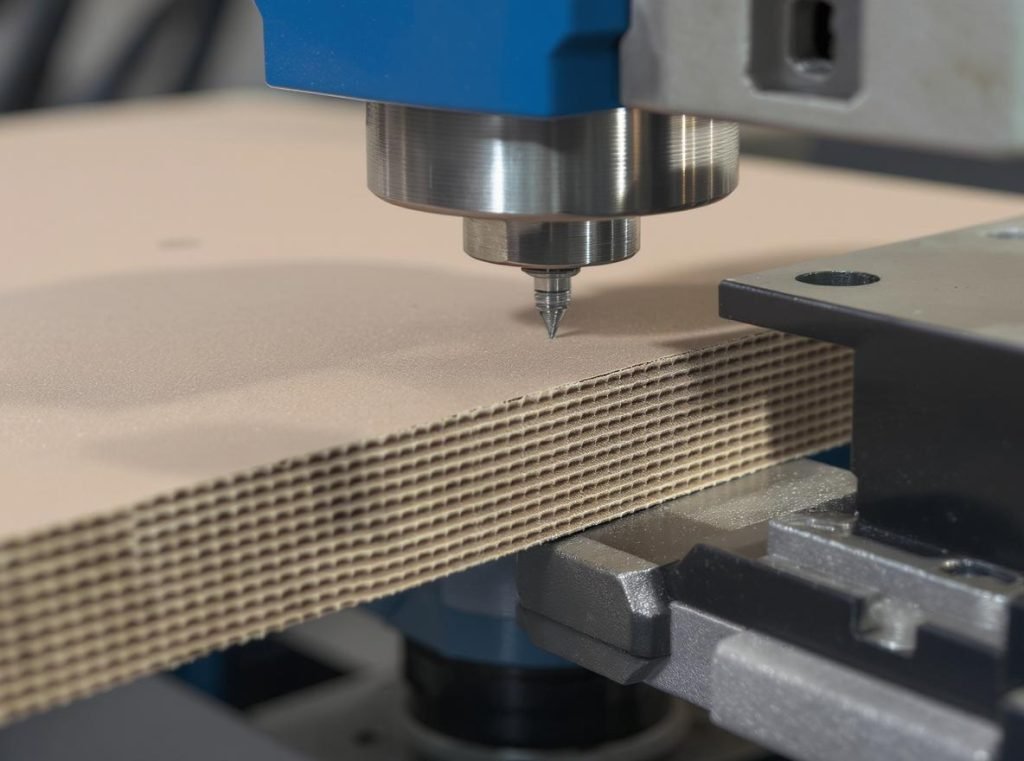
The testing process follows precise international standards including TAPPI T838, TAPPI T811, ISO 3037, and ASTM D7336. Here’s how the measurement works:
Sample Preparation:
- A 50mm x 100mm specimen is carefully cut from the corrugated material
- Edges are often wax-dipped to prevent splitting during testing
- Samples are conditioned in controlled humidity and temperature environments
Testing Procedure:
- The specimen is positioned vertically between compression platens
- Force is gradually applied perpendicular to the flute direction
- The maximum force before material failure is recorded as the ECT rating
The edge crush resistance is calculated using the formula: R = 0.01 × F̄max, where F̄max represents the mean maximum force in newtons. This standardized approach ensures consistent results across different laboratories and manufacturers worldwide.
| ECT Rating | Force Resistance | Material Thickness | Typical Wall Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 23 ECT | 23 lbs per inch | 0.125″ | Single-wall |
| 32 ECT | 32 lbs per inch | 0.156″ | Single-wall |
| 44 ECT | 44 lbs per inch | 0.188″ | Single-wall |
| 48 ECT | 48 lbs per inch | 0.250″ | Double-wall |
How Do Different ECT Ratings Impact Box Strength?
ECT ratings create a direct correlation between test values and real-world box performance, with higher ratings providing exponentially better stacking capabilities and load distribution.
Common ECT ratings range from 23 ECT for lightweight applications to 71 ECT for heavy-duty industrial use. The relationship between ECT rating and box performance follows the McKee Formula: BCT = 5.876 × ECT × √(U × d), where BCT is box compression strength, U is box perimeter, and d is board thickness.
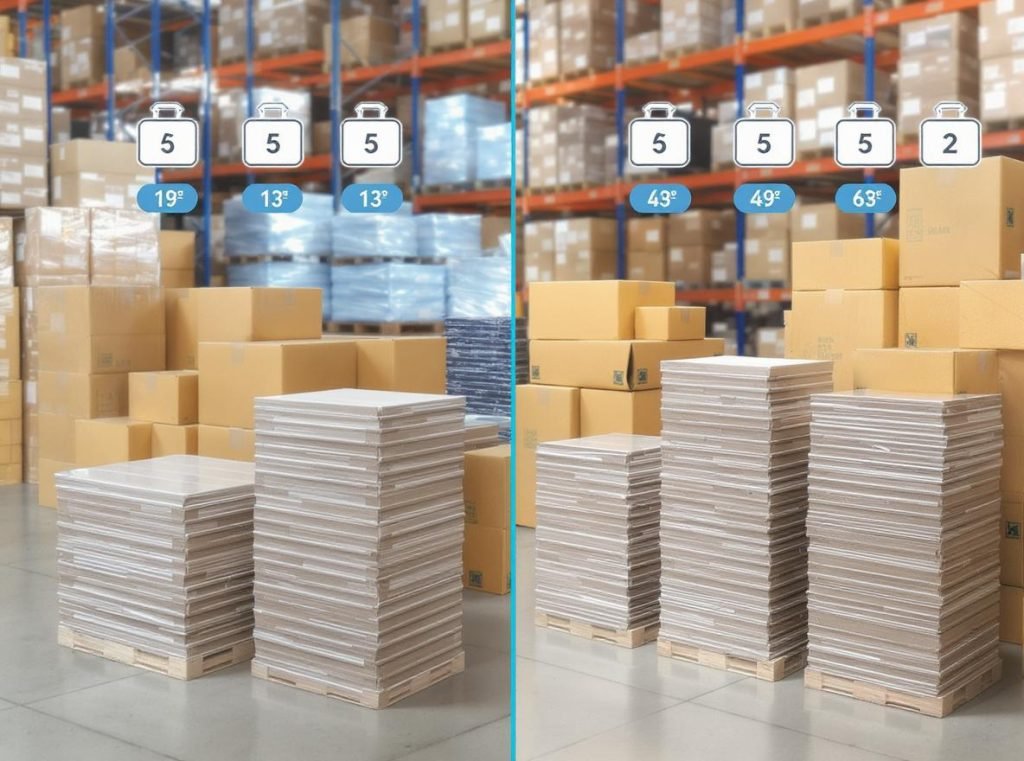

Different ECT ratings serve distinct purposes in packaging applications:
23 ECT – Light-Duty Applications:
Suitable for products weighing 20-25 pounds with minimal stacking requirements. Perfect for documents, small parts, and lightweight consumer goods that won’t be subjected to heavy warehouse stacking.
32 ECT – Industry Standard:
The most commonly used rating, handling products up to 35-40 pounds and providing excellent cost-performance balance. This rating meets most carrier requirements and works well for general e-commerce shipping.
44 ECT – Heavy-Duty Performance:
Designed for products weighing 50-65 pounds with significant stacking requirements. Ideal for retail distribution, warehouse storage, and products that experience rough handling during transit.
48+ ECT – Maximum Strength:
Reserved for the heaviest applications, supporting 65-80+ pounds with exceptional stacking capabilities. Often used in double-wall construction for industrial shipping and specialized applications.
The performance differences become dramatic when considering stacking scenarios:
| Stacking Height | 32 ECT Load Capacity | 44 ECT Load Capacity | 48 ECT Load Capacity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1-2 boxes high | 100% rated capacity | 100% rated capacity | 100% rated capacity |
| 3-4 boxes high | 75% rated capacity | 90% rated capacity | 95% rated capacity |
| 5+ boxes high | 50% rated capacity | 75% rated capacity | 85% rated capacity |
Why Is ECT More Important Than Other Strength Tests?
The packaging industry has shifted decisively toward ECT testing because it provides superior real-world performance prediction compared to traditional testing methods.
ECT measures actual stacking strength rather than puncture resistance, making it the preferred standard for today’s palletized shipping and warehouse storage systems. Research shows that ECT-specified materials are 4.3% more cost-effective and 17.5% lighter than equivalent Mullen Burst Test specifications while providing better performance correlation.
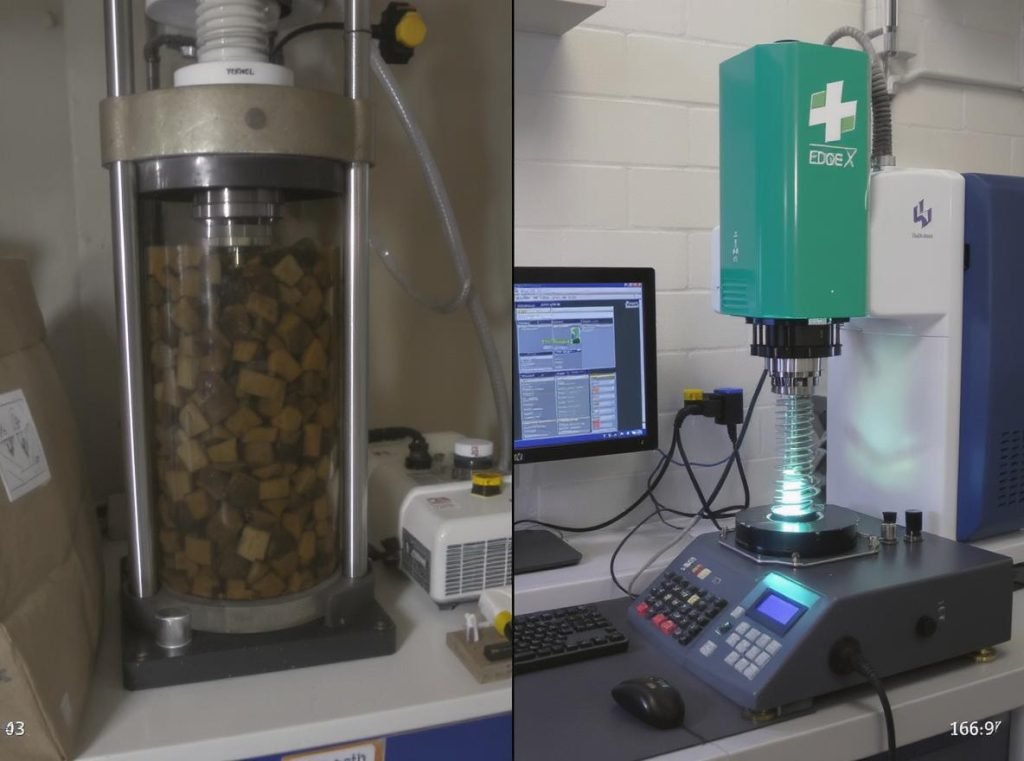

The advantages of ECT over traditional Mullen Burst Testing include:
Performance-Based Measurement:
ECT directly measures the forces that boxes encounter in real shipping environments – vertical compression from stacking. This makes it far more predictive of actual box performance than puncture resistance tests.
Material Efficiency:
ECT testing enables manufacturers to optimize material usage by focusing on the strength characteristics that matter most. This allows for lighter packaging without compromising protection, supporting sustainability goals.
Recycled Content Compatibility:
As the industry moves toward greater use of recycled materials, ECT testing works effectively with recycled corrugated content, while Mullen testing often showed poor correlation with recycled materials.
Modern Logistics Alignment:
Today’s supply chains rely heavily on palletized shipping, automated warehousing, and high-density storage – all scenarios where vertical compression strength is critical.
The shift to ECT has been so pronounced that many major shipping companies now specify ECT ratings rather than Mullen ratings in their packaging requirements.
What ECT Rating Should You Choose for Your Products?
Selecting the appropriate ECT rating requires careful analysis of your specific shipping requirements, product characteristics, and supply chain conditions.
The most common ECT ratings are 32 ECT, 44 ECT, and 48 ECT, chosen based on product weight, stacking requirements, and handling conditions. The general rule is to select an ECT rating that can handle 1.5-2 times your product weight to provide adequate safety margin.
Consider these critical factors when making your selection:
Product Weight Analysis:
- Light products (0-25 lbs): 23-32 ECT typically sufficient
- Medium products (25-50 lbs): 32-44 ECT recommended
- Heavy products (50+ lbs): 44+ ECT or double-wall construction required
Stacking Requirements:
Determine maximum stacking height in your distribution network. Higher stacks require proportionally higher ECT ratings to prevent compression failure at the bottom boxes.
Transportation Conditions:
- Regional shipping: Lower ECT ratings may suffice
- Long-distance shipping: Higher ECT ratings for extended stacking periods
- International shipping: Maximum ECT ratings for extended transit times
Environmental Factors:
Humidity and temperature variations can reduce box strength by 20-30%. Consider upgrading ECT ratings for challenging climate conditions.
Here’s a practical selection guide based on industry best practices:
| Your Application | Product Weight | Recommended ECT | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-commerce, light items | 0-25 lbs | 32 ECT | Cost-effective, meets carrier minimums |
| Retail distribution | 25-50 lbs | 44 ECT | Good stacking strength, warehouse suitable |
| Industrial shipping | 50+ lbs | 48+ ECT | Maximum protection, heavy stacking loads |
| Fragile items | Any weight | +1 ECT rating | Additional protection margin |
How Does ECT Rating Affect Your Packaging Costs?
ECT ratings create a complex cost equation where higher ratings increase material costs but often reduce total logistics expenses through improved performance.
Higher ECT ratings typically increase material costs by 15-30% compared to lower ratings, but this investment often pays for itself through reduced damage rates, improved stacking efficiency, and lower total cost of ownership. The key is finding the optimal balance between upfront costs and performance benefits.
The comprehensive cost analysis includes:
Material Cost Impact:
- 32 ECT vs 26 ECT: 15-25% cost increase
- 44 ECT vs 32 ECT: 20-30% cost increase
- 48 ECT vs 44 ECT: 10-15% cost increase
Shipping Weight Considerations:
Higher ECT ratings require more material, increasing box weight by 10-20%. This affects shipping costs, especially for dimensional weight pricing.
Damage Prevention Benefits:
- 32 ECT: 20-30% reduction in damage rates vs lower ratings
- 44 ECT: 30-40% reduction in damage rates vs 32 ECT
- 48 ECT: 40-50% reduction in damage rates vs 44 ECT
Hidden Cost Savings:
- Reduced repackaging and handling costs
- Lower insurance claims and customer service issues
- Improved inventory management through standardization
- Better space utilization in shipping containers
| Cost Category | Impact of Higher ECT | Long-term Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Material costs | +15-30% | Standardized inventory |
| Shipping costs | +5-12% | Reduced damage claims |
| Labor costs | -10-15% | Faster handling, fewer returns |
| Total Cost | +5-15% | Positive ROI in 6-12 months |
What Are the Testing Standards and Regulations for ECT?
ECT testing operates under strict international standards that ensure consistency, reliability, and comparability across global supply chains.
ECT testing follows established protocols including TAPPI T838 for short column testing, TAPPI T811 for edgewise compression, ISO 3037 for international harmonization, and ASTM D7336 for US-based applications. These standards specify exact procedures for sample preparation, testing conditions, and result interpretation.

Key testing standards and their applications:
TAPPI T838 – Short Column Test:
- Primary standard for ECT testing in North America
- Uses 50mm x 100mm samples with wax-dipped edges
- Conducted under controlled humidity conditions
- Provides most accurate correlation with box performance
ISO 3037 – International Standard:
- Harmonized global testing method
- Enables consistent results across different countries
- Critical for international shipping and trade
- Supports quality assurance in global supply chains
Quality Control Requirements:
Regular calibration and validation ensure testing accuracy. TAPPI T1200 defines specific repeatability and reproducibility standards that laboratories must meet.
Compliance Considerations:
- Carrier requirements for minimum ECT ratings
- Industry-specific regulations for certain product categories
- International shipping standards for export markets
- Documentation requirements for quality assurance
At Acreet, we maintain comprehensive testing capabilities that exceed international standards, ensuring your custom packaging meets all relevant ECT requirements while optimizing performance for your specific applications.
How Can You Optimize Box Performance Beyond ECT Ratings?
While ECT ratings provide the foundation for box strength, achieving optimal packaging performance requires a holistic approach that considers design, materials, and operational factors.
ECT rating is just one element of total packaging performance. Box design, flute structure, adhesive quality, and environmental controls all contribute to real-world packaging effectiveness and can significantly impact your bottom line.
Advanced optimization strategies include:
Flute Structure Selection:
Different flute profiles offer varying strength characteristics. A-flute provides maximum cushioning, C-flute offers best printing surface, and E-flute enables compact stacking with good crush resistance.
Adhesive Quality Management:
High-quality adhesives ensure proper bonding between corrugated layers, maintaining structural integrity throughout the shipping cycle. Poor adhesive can reduce effective ECT performance by 15-25%.
Box Design Optimization:
- Proper corner reinforcement and flap overlap
- Optimal length-to-width ratios for stacking efficiency
- Strategic placement of score lines and perforations
- Integration of internal dividers and cushioning
Environmental Controls:
Humidity management is critical – every 10% increase in relative humidity can reduce box strength by 5-10%. Temperature variations also affect adhesive performance and material stability.
Advanced Testing Integration:
Combine ECT testing with Box Compression Testing (BCT) to validate actual box performance. BCT testing provides real-world validation of ECT predictions under specific loading conditions.
| Optimization Factor | Performance Impact | Implementation Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Flute selection | 10-15% strength variation | Match flute to application needs |
| Adhesive quality | 15-25% strength impact | Specify high-quality bonding agents |
| Design geometry | 20-30% efficiency gain | Optimize ratios for stacking |
| Environmental control | 5-10% strength preservation | Climate-controlled storage |
What Future Trends Are Shaping ECT Testing?
The ECT testing landscape is evolving rapidly with technological advances, sustainability demands, and changing market requirements driving innovation.
Digital transformation, sustainability initiatives, and Industry 4.0 integration are revolutionizing ECT testing with IoT monitoring, AI-powered analysis, and automated testing systems. The global ECT testing market is projected to grow at 7-8% CAGR through 2035, driven by increasing quality assurance demands and regulatory compliance requirements.

Emerging technological trends include:
Digital Integration:
- Real-time monitoring during testing with IoT sensors
- AI-powered analysis for predictive performance modeling
- Automated testing systems reducing human error
- Cloud-based data sharing for enhanced collaboration
Sustainability Innovation:
- Advanced bio-based materials requiring new testing protocols
- Recycled content optimization while maintaining ECT performance
- Circular economy design principles for end-of-life considerations
- Carbon footprint reduction through optimized material usage
Smart Packaging Evolution:
Integration of sensors and monitoring capabilities directly into packaging, enabling real-time performance tracking throughout the supply chain.
Predictive Analytics:
Machine learning algorithms that can predict box performance based on ECT ratings, environmental conditions, and handling scenarios, enabling proactive packaging optimization.
Advanced Testing Equipment:
- Portable testing devices for on-site quality control
- Multi-frequency testing for complex material analysis
- Enhanced sensor technology for improved accuracy
- Automated data collection and analysis systems
These innovations create significant opportunities for packaging professionals to reduce costs, improve performance, and meet sustainability goals while maintaining the highest standards of product protection.
Summary
ECT ratings directly determine your corrugated box’s vertical load capacity and stacking strength, making them essential for effective packaging design and supply chain optimization. Understanding how different ECT ratings affect performance helps you balance cost, protection, and sustainability while ensuring your products arrive safely at their destination.

Ready to optimize your packaging performance with the right ECT rating? Contact Acreet today for expert consultation on custom packaging solutions. Our team combines deep technical knowledge with practical experience to help you select the perfect ECT rating for your specific needs, ensuring maximum protection at optimal cost. Let us help you design packaging that performs reliably while supporting your business goals.


